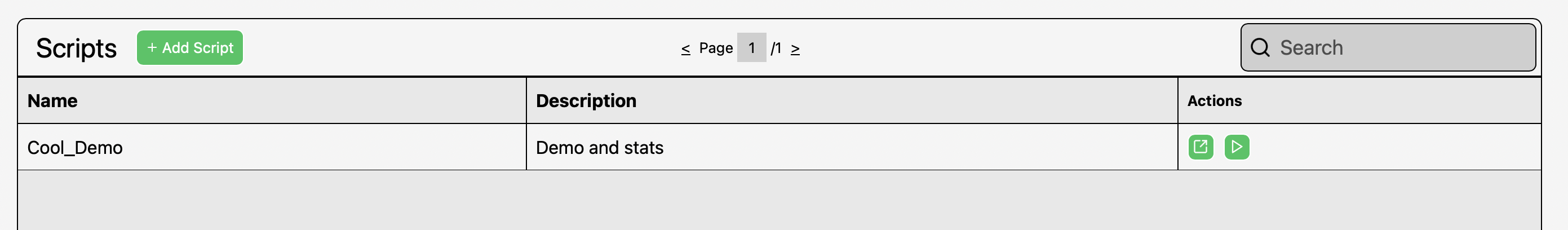
Run MikroTik scripts across your entire fleet — safely, quickly, and consistently.
Script Commander is an Admiral Platform automation feature that allows users to upload MikroTik script files (.rscformat), store and organize them with friendly nicknames, and execute these scripts across selected routers on demand or on a scheduled basis. Script Commander provides a centralized, scalable method to deploy changes, fix configurations, enforce standards, or run maintenance workflows across any size network.
This feature eliminates the need to manually log in to each router, reduces human error, and provides an auditable workflow for network configurations. It also allows for use of special characters that may not work in the existing Fleet Commander interface in Admiral.
Key Capabilities of Script Commander #
- Upload MikroTik script files (
.rsc) - Assign each script a nickname for easier identification
- Store multiple scripts in a centralized library
- Create Script Commander jobs
- Run the same script on one or more MikroTik routers
- Track script execution status, results, and logs
- Provide audit history of all script deployments
Prerequisites #
Before using Script Commander:
- The target MikroTik routers are online in Admiral.
- The device has Admiral VPN active or permitted API/SSH access.
- Scripts must be RouterOS-compatible, properly formatted, and safe for production use.
Add a Script #
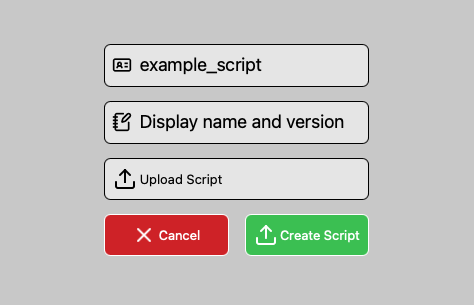
Navigate to Router List → Fleet Commander → Script Commander.
Click Add Script.
Select a .rsc file from your computer.
Enter a Nickname for the script
Example:
- “Reboot All CAPs”
- “Add VLAN 20 to Bridge”
- “BGP Peering Fix – v2”
Add a description for internal documentation.
Click Create Script.
Your script now appears in your Script Library and can be used anytime.
Creating a Script Commander Job #
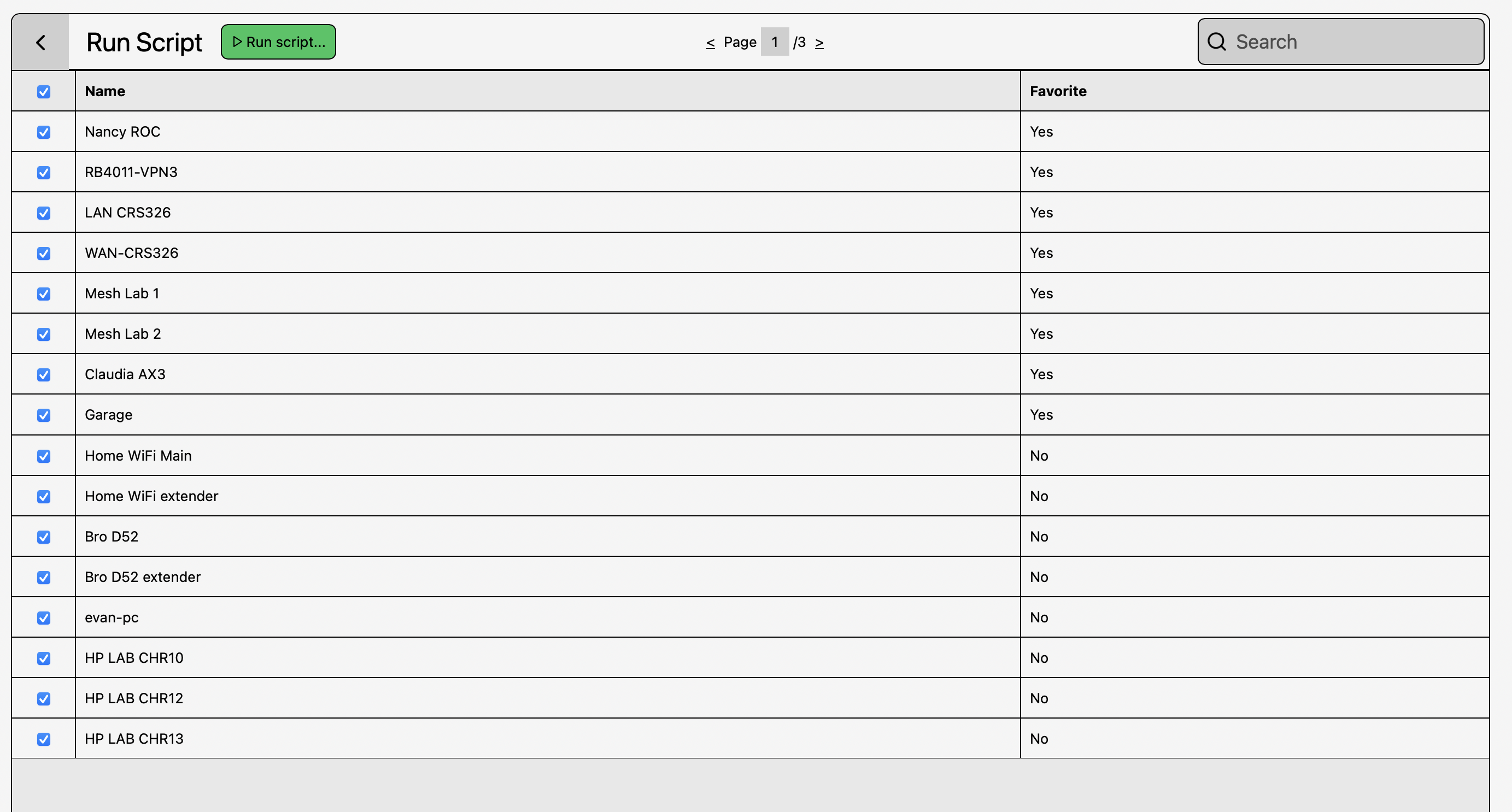
Navigate to Router List → Fleet Commander → Script Commander
Select a script from your Script Library.
Select target routers:
- Use search filters (site, tag, model, OS version, etc.)
- Multi-select routers
- Bulk “Select All” option
Confirm & execute.
Job Execution Process #

When a Script Commander job runs:
- Admiral opens a secure execution channel to each router.
- The
.rscfile is pushed to the device. - RouterOS executes the script line-by-line.
- Admiral captures:
- Exit status
- Return output (if applicable)
Example Use Cases #
- Deploy global firewall policy updates
- Push VLAN/bridge configuration changes
- Add DHCP options network-wide
- Update NTP or DNS settings
- Mass-reboot for scheduled maintenance
- Apply emergency hotfix scripts
- Replace or remove static routes
- Reset wireless channels or DFS profiles
Script Best Practices #
To ensure safe, predictable operation:
- Always test scripts in a lab router first.
- Use conditional statements (
:if) to prevent misconfigurations. - Avoid destructive commands unless necessary (e.g.,
reset-configuration). - Comment your scripts with notes and version tags.
- Avoid hard-coded interfaces unless consistent across your fleet.
- Keep scripts small and modular.
Common Errors & How to Fix Them #
| Error Example | Meaning | How to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Failed – Router offline | Router was not reachable | Ensure device is online in Admiral |
| Script error | Command inside script failed | Review syntax or update for RouterOS version |
| Permission denied | Script tried a restricted operation | Verify user permissions |
| No output | Script ran silently | Add :put or :log info inside script |
Frequently Asked Questions #
❓ Does Script Commander make permanent changes? #
Yes — if your script includes configuration commands.
If the script only prints information (:put, :log) then it is safe and read-only.
❓ Do I need MikroTik scripting experience? #
No — you can upload pre-made .rsc files or use Script Commander’s examples.
❓ Will other team members see my scripts? #
Yes, unless restricted by your role permissions.
Demo Status Dashboard (Safe) #
# Cool Status Dashboard (Safe)
:put "──── Router Dashboard ────"
:put ("Name: ". [/system identity get name])
:put ("Version: ". [/system resource get version])
:put ("Uptime: " . [/system resource get uptime])
:put "────────────────────────────"
:log info "Script Commander: Dashboard script ran successfully"
Additional Script Tips #
- Use :global instead of :local for setting variables.
- Use :log to see output
- Use
"for strings and not' - Escape variables with a backslash : example
\$inTime





