Follow this guide to add a Linux host to your Admiral Platform WatchTower deployment. Monitoring is built to be simple, lightweight, and quick to deploy.

WatchTower Linux Requirements #
MikroTik Connectivity #
Admiral Platform’s pull-based monitoring model leverages MikroTik devices to connect our dashboard to your Linux devices. Before you can add a Linux device, the MikroTik it is connected to must be added to your dashboard. Follow this guide to add a MikroTik device to your dashboard before you get started:
Here is our guide on Adding MikroTik Devices
The Linux device must have IP reachability to the MikroTik for it to be added to your dashboard. Usually this means direct connectivity as a neighbor, but tunnels, management VRF, and other more advanced methods will work, but may require additional configuration that is not covered in this guide.
At minimum, connection tracking must be enabled, and there must be a standard masquerade rule. These are both present on a MikroTik with the default configuration (defconf) so you can quickly connect a default MikroTik to start using our service.
Admiral’s cloud-based service requires a MikroTik with connectivity. If you do not have physical MikroTiks, there are three standard options:
The easiest option is to add a physical MikroTik to your network, with the default configuration. Admiral Platform is very lightweight, so a compatible device may cost less than $100.
A VM-based MikroTik Cloud Hosted Router can also be added to your Admiral deployment and used to connect to your Linux devices. If you do not have experience with MikroTiks, contact our sales team about a CHR Setup Consulting Block.
If you have a larger deployment, a dedicated on-premise Admiral deployment has a MikroTik CHR built-in and in certain situations can be connected directly to your Linux nodes. Contact our sales team for more information on dedicated deployments.
Additionally, options such as SSH forwarding, TURN servers, and more advanced solutions may operate as expected but are not covered in this documentation.
Linux Kernel Version #
Thanks to SNMP, many versions of the Linux Kernel are supported. It is very likely your distribution is compatible with WatchTower, as long as you can install the snmpd package, which has requirements listed below.
Our engineers have successfully onboarded multiple kernel versions, hypervisors powered by Linux such as ProxMox, and even some Unix-Like OS’s that support snmpd such as OpenBSD. If you are running into trouble and believe it is related to your kernel version or distribution, please contact our support team with system details.
LinuxNetSNMP (snmpd) #
- Only required if using WatchTower for SNMP Monitoring
- SNMP version: v2c only
- snmpd version: 5.0 and newer
If this is your first time working with SNMP, we recommend familiarizing yourself with configuring SNMP on your devices before you add them to your dashboard. The following steps are provided as a courtesy and may be different from your configuration.
SNMP Configuration #
Add or modify the following lines of configuration to your snmpd.conf file:
Example OID Include Statement: #
view systemonly included .1.3.6.1For more information on the OIDs we use, view our full list here.
Accurate Memory Graphs #
We recommend adding the following line below your include statement for the most accurate memory usage:
extend SReclaimable /usr/bin/grep SReclaimable /proc/meminfoAllow Remote Access #
Your SNMP configuration may only allow local communication by default. Use the following line to allow all external communication over UDP port 161. You can further restrict access as long as communication is allowed from your MikroTik.
agentaddress udp:161,udp6:[::1]:161SNMP Community Secret #
It is best practice to use a unique community secret to secure your devices. Locate the following lines in your config and change the word “public” to the secret that you want to use. You will use this secret later when on-boarding your devices so that our servers can access them via SNMP.
rocommunity public default -V systemonly
rocommunity6 public default -V systemonlyMake sure to restart SNMP after updating your config
systemctl restart snmpdsnmpd commands #
Check your snmpd version using this command:
snmpd -vMissing snmpd? Install it using your package manager: #
apt for Debian-based
apt install snmpdyum OR dnf for RedHat-based
yum install net-snmppacman for Arch-based
pacman -S snmpdEnable & Start SNMP #
Enable SNMP once installed
systemctl enable snmpdStart SNMP if it is not already running
systemctl start snmpdSSH Server (sshd) #
- Only required if using WatchTower for remote access through Web SSH
- Supports any SSH server that conforms to SSH standards
- Password and Key-based logins are supported
- Interactive login is NOT supported
sshd Configuration #
There are so many options for configuring an SSH Server, we are unable to cover them in this guide. We recommend becoming familiar with sshd configuration and investigating security measures such as disabling remote root login, preventing empty passwords, whitelisting specific users, or requiring key login.
sshd commands #
Check your sshd version using this command:
sshd -V localhostMissing sshd? Install it using your package manager: #
apt for Debian-based
apt install openssh-serveryum OR dnf for RedHat-based
yum install openssh-serverpacman for Arch-based
pacman -S opensshEnable & Start SSHD #
Enable SNMP once installed
systemctl enable sshdStart SNMP if it is not already running
systemctl start sshdAdd a Linux device to WatchTower #
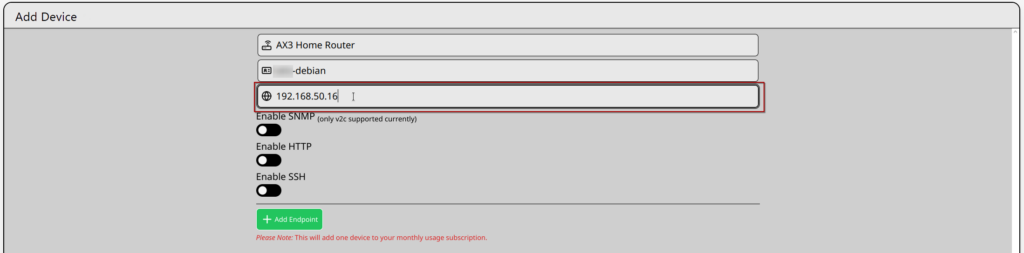
- Using the left menu, navigate to the WatchTower page
- Click on the green “Add Device” button
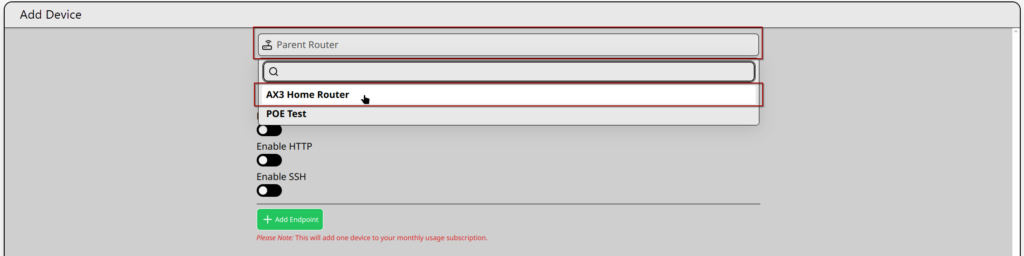
- In the “Parent Router” box, search and select the MikroTik that the device is connected to
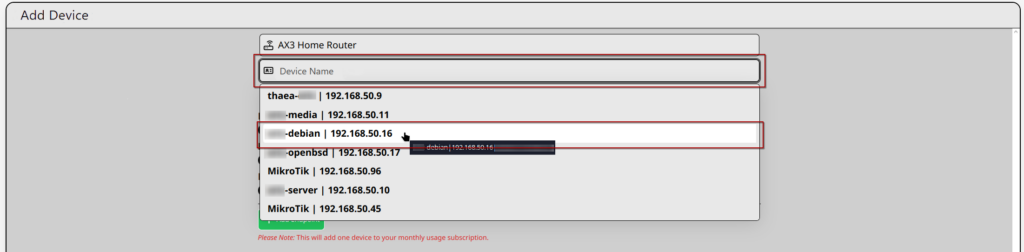
- Click the “Device Name” box. A quick-select menu appears with any detected Linux devices. Selecting one also fills in the IP address.
- If you do not see the device you want to add, you can type a custom name and IP.
- You may rename a device in the Device Name box one you have picked it from the quick-select menu.
- If you do not see the device you want to add in the “Device Name” list, you can enter it’s IP into the IP Address Box.
- If you used the quick-select menu, verify the IP Address before you continue.
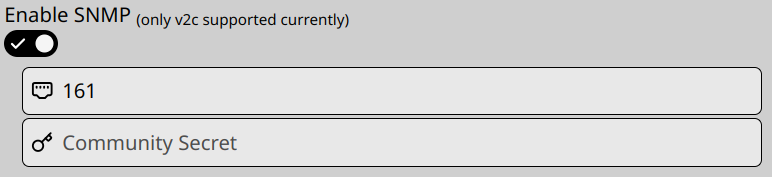
Enable SNMP Monitoring #
- If you have configured SNMP on your device, WatchTower can generate graphs and alert on CPU, RAM, DISK, and Networking metrics.
- For monitoring features, click on the “Enable SNMP” Slider
- The default SNMP port is 161. If you have modified this port, update it here.
- There is an edit page for making changes later.
- If this device is configured with an SNMP Community Secret, enter it in the “Community Secret” box.
- Admiral recommends utilizing a community secret for best security practices.
- The default SNMP port is 161. If you have modified this port, update it here.
Admiral Platform WatchTower currently only supports SNMP v2c, which uses community secrets. If you have a username and password, this either means you are using SNMP v3 which is not supported, or you are confusing the SNMP authentication with a Linux User authentication, which are managed separately. If your security policy allows it, you can usually quickly configure SNMP with a community secret and allow v2c communication if you wish to use our monitoring platform.
Enable HTTP Monitoring #
- If your Linux node is running a web server such as Apache or nginx, WatchTower can monitor HTTP and HTTPS status codes.
- For HTTP Status Code Monitoring, click on the “Enable HTTP” Slider
- Enter your web server URL into the HTTP URL box
- Your URL must include either http:// OR https://
- Not using the standard port? Make sure to include it after the domain
- Examples:
- http://admiralplatform.coml/blog-page/
- https://app.remotewinbox.com:8080/auth/users/auth/login
- Enter your web server URL into the HTTP URL box

Enable Web SSH #
- If you have configured an SSH server on your device, WatchTower can create a terminal in your browser for remote access and file transfer through SFTP.
- For remote access, click on the “Enable SSH” Slider
- The default SSH port is 22. If you have modified this port, update it here.
- There is an edit page for making changes later.
- The default SSH port is 22. If you have modified this port, update it here.
You do not need to enter any authentication when setting up a device in WatchTower, you will instead enter authentication every time you open a new Web SSH session.

- Once you have reviewed the entered information, select the “Add Device”. Admiral Platform WatchTower will add required firewall rules to your MikroTik, check for connectivity, and display any errors.

- Once successful, you will be redirected to the WatchTower page, with your new device added to the list!
- After 5 minutes, polling data will begin to populate your dashboard for your new device.

What is WatchTower capable of? #
Check out an overview of WatchTower Features here!
Troubleshooting WatchTower #
General Steps #
- Double check that all information is entered correctly.
- Make sure that the device is reachable from from the MikroTik.
- You may need to double check both the MikroTik and Linux firewalls allow traffic.
- Confirm that the MikroTik is online. If it is not reachable from the dashboard, you won’t be able to add devices through it.
Error: Either SSH, HTTP, or SNMP are required… #
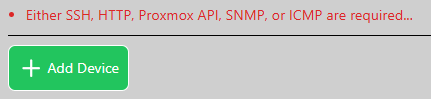
- This notice appears when you click on the “Add Device” button without enabling SSH, HTTP, or SNMP.
- When adding a device, you must either Enable SNMP, HTTP, or SSH. WatchTower will not let you add a device without first selecting one of these options.
Error: Connecting to SNMP failed #
- This error indicated our servers were not able to connect to the device over SNMP.
- Are the port and community secret correct?
- Are the MikroTik and Linux node online?
- Does the MikroTik allow traffic from the Admiral servers to reach the Linux device?
- Does the Linux device allow traffic through its firewall?
- Is SNMP configured to allow external connections?
- Is the community secret configured in the SNMP configuration?
- Are you using SNMP v2c?
Error: Connecting to HTTP failed #

- This error indicates our servers were not able to connect to the device over HTTP.
- Is the URL entered correctly?
- Are you using a unique port? Make sure to add it to the URL.
- http://admiralplatform.coml/blog-page/
- https://app.remotewinbox.com:8080/auth/users/auth/login
- Are the MikroTik and Linux node online?
- Does the MikroTik allow traffic from the Admiral servers to reach the Linux device?
- Is the web server configured and enabled?
Error: URL should be a valid http(s) URL. #

- This error indicates the URL you have entered isn’t formatted correctly.
- URL must begin with either http:// or https://
- If you are not using a standard port, make sure to add it with a colon.
- http://example.local/test
- https://example.lan:8080/homepage
Error: Connecting to SSH failed #
- This error indicates our servers were not able to connect to the device over SSH.
- Is the port correct?
- Are the MikroTik and Linux node online?
- Does the MikroTik allow traffic from the Admiral servers to reach the Linux device?
- Does the Linux device allow traffic through its firewall?
- Is SSH configured allow external connections?
Want to learn more about Admiral Platform? Check out our YouTube channel!




